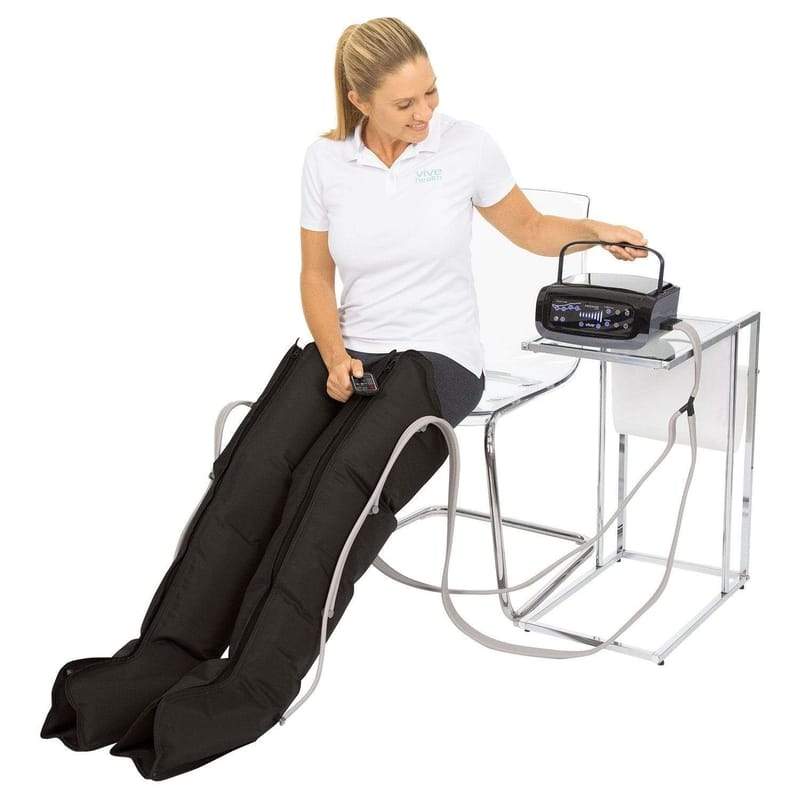


A short time later, the pressure is reduced, allowing increased blood flow back into the limb. When activated, the pump fills the air chambers of the jacket in order to pressurize the tissues in the limb, thereby forcing fluids, such as blood and lymph, out of the pressurized area. In use, an inflatable jacket (sleeve, glove, trousers or boot) encloses the limb requiring treatment, and pressure lines are connected between the jacket and the air pump. 2012 141(Suppl 2):195–226.Intermittent pneumatic compression is a therapeutic technique used in medical devices that include an air pump and inflatable auxiliary sleeves, gloves or boots in a system designed to improve venous circulation in the limbs of patients who have edema or the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), or the combination of DVT and PE which is venous thrombeombolism (VTE). Prevention of VTE in nonsurgical patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Kahn SR, Lim W, Dunn AS, Cushman M, Dentali F, Akl EA, Cook DJ, Balekian AA, Klein RC, Le H, Schulman S, Murad MH. Venous thromboembolism: a public health concern. Surveillance for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: recommendations from a national workshop. Raskob GE, Silverstein R, Bratzler DW, Heit JA, White RH. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients vs community residents. Heit JA, Melton LJ 3rd, Lohse CM, Petterson TM, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN, O’Fallon WM. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. Sequential compression devices Venous thromboembolism Hospitalized patients Effectiveness. Yatış süresince SCD grubunda NONE grubu ile karşılaştırıldığında VTE insidansında bir azalma gözlenmemiştir. Riske göre düzeltilmiş analiz SCD grubu ve NONE grubu arasında VTE insidansında anlamlı bir farklılık göstermemiştir (odds oranı 0,99, %95 güven aralığı 0,57-1,73, p=0,74). SCD kullanılan 20,018 hastadan 47’sinde (41 DVT, 6 PE), SCD kullanmayan 10,819 hastanın 20’sinde (14 DVT, 6 PE) VTE görüldü. VTE riski, hastanede yatış süresi ve diğer komorbiditeler eğilim skoru eşlenmiş SCD grubu ve tromboproflaksi kullanmayan grup (NONE) için analiz edilmiştir.ģ0,824 hastadan 67 hasta (%0,22) hastanede yatış süresi içinde VTE geçirdi, bunların 55 tanesi derin ven trombozu (DVT), 12 tanesi pulmoner emboli (PE) idi. Antikoagülan tedavi alanlar, SCD kullanılsın ya da kullanılmasın, çalışma dışında bırakılmıştır. Çalışmaya Nisan 2015 ile Mart 2016 tarihleri arasında eğitim hastanesine yatan erişkin hastalar alınmıştır. Çalışmanın amacı hastanede dahili hastalıklar nedeniyle yatan hastalarda ardışık kompresyon cihazlarının (SCD) venöz tromboemboliyi (VTE) önlemedeki etkinliğinin değerlendirilmesidir. Risk-adjusted analysis showed no significant difference in VTE incidence in the SCD group compared to NONE (odds ratio 0.99, 95% confidence interval 0.57-1.73, p=0.74).Ĭompared to the NONE group, SCDs are not associated with decreased VTE incidence during hospital stay. VTE was seen in 47 out of 20,018 patients on SCDs (41 DVT, 6 PE) and 20 out of 10,819 patients without SCDs (14 DVT, 6 PE). We analyzed VTE risk, length of hospital stay, and other comorbidities among propensity score-matched patients on SCDs and those without thromboprophylaxis (NONE).Īmong 30,824 patients, 67 patients (0.22%) developed VTE during their hospital stays, with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in 55 cases and pulmonary embolism (PE) in 12. Patients on anticoagulants with or without SCDs were excluded.
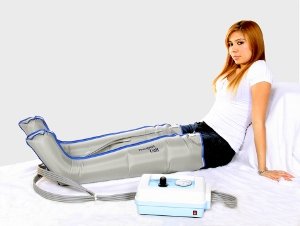
To evaluate the effectiveness of sequential compression devices (SCDs) for venous thromboembolism (VTE) prevention in medically ill hospitalized patients.Īdult patients admitted to a teaching hospital from April 2015 to March 2016 were included.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
